Book Appointment Now

Graphics Card PCI-E 6-Pin & 8-Pin Connectors Tutorial
Graphics Card PCI-E 6-Pin & 8-Pin Connectors Tutorial
The 6-pin connector can supply up to 75 watts, while the 8-pin connector can deliver up to 150 watts. Some high-end cards even require two or three 8-pin connectors. Incorrectly connecting or underpowering a GPU can lead to instability, crashes, and ultimately, hardware failure. Therefore, understanding the power requirements of your chosen graphics card and ensuring your PSU has sufficient connectors and wattage is crucial for building a stable and long-lasting system.
In this section, I’ll go through the graphics card’s power requirements as well as its specific PCI-E power ports. Every modern graphics card features a PCI Express x16 connector that interfaces with your motherboard. This slot doesn’t just handle data communication; it also delivers power. A standard PCI Express x16 slot can deliver a maximum of 75 Watts to the graphics card. This is sufficient for low-profile and budget GPUs (like the GTX 1050 Ti or RX 550), but powerful cards need significantly more juice.
Understanding Power Limits
When a card needs more than the 75W the motherboard provides, it utilizes external power connectors. Here is the breakdown:
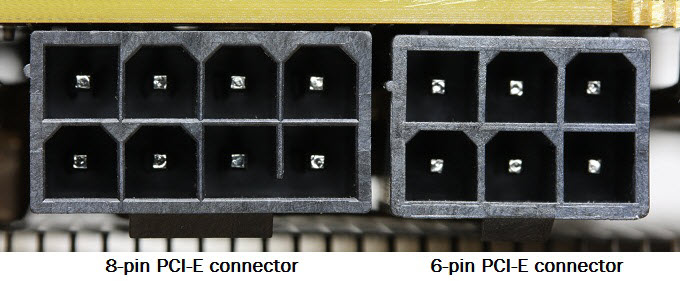
The 6-Pin Connector (75 Watts)
A single 6-pin power connector can deliver up to 75 watts. If your graphics card’s total power consumption is greater than 75W but less than 150W, it will typically use the motherboard slot power (75W) plus one 6-pin connector (75W), for a total theoretical maximum of 150 Watts. The majority of mid-range graphics cards from Nvidia and AMD utilize this configuration.
The 8-Pin Connector (150 Watts)
For more demanding cards, the 8-pin connector is used. This connector can deliver up to 150 watts on its own. When combined with the motherboard slot, a card with a single 8-pin connector can draw up to 225W total.
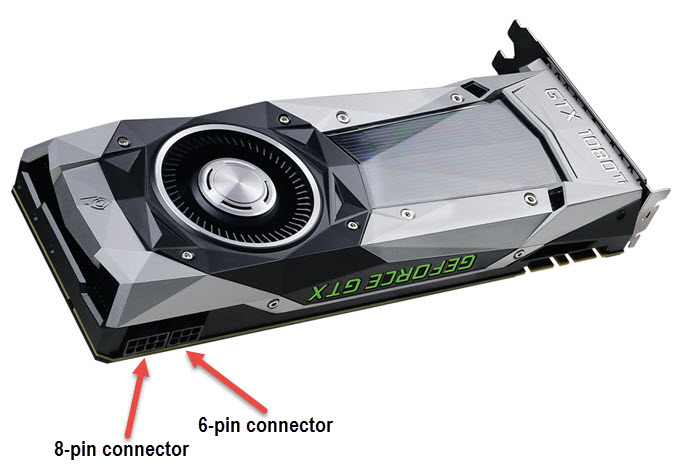
Top-tier graphics cards (like the RTX 3080 or RX 6900 XT) often require multiple connectors, such as two 8-pin connectors or even three, to support power draws exceeding 300W. If your PSU lacks these specific cables, you may need to look into adapters, though native cables are always safer.
Check out the Best Power Supply for High-End Graphics Cards to ensure you have the native cables you need.
Power Adapters: A Solution for Older PSUs
If you have an older power supply that lacks the necessary PCI-E connectors, you can use adapters. However, caution is advised: ensure your PSU has enough total wattage on the 12V rail to support the card before using adapters.
1. 4-Pin Molex to 6-Pin PCI-E Adapter

If your graphics card requires a 6-pin power connector but your PSU only has legacy Molex connectors, this adapter is the standard solution. Ideally, use an adapter that connects to two separate Molex strands to ensure sufficient current flow without overheating the wires.
2. 4-Pin Molex to 8-Pin PCI-E Adapter

This adapter combines two standard 4-pin Molex connectors to create a single 8-pin PCIe power connector. This is suitable for mid-range to high-end cards, provided your PSU has the amperage to back it up.
3. 6-Pin to 8-Pin PCI-E Adapter
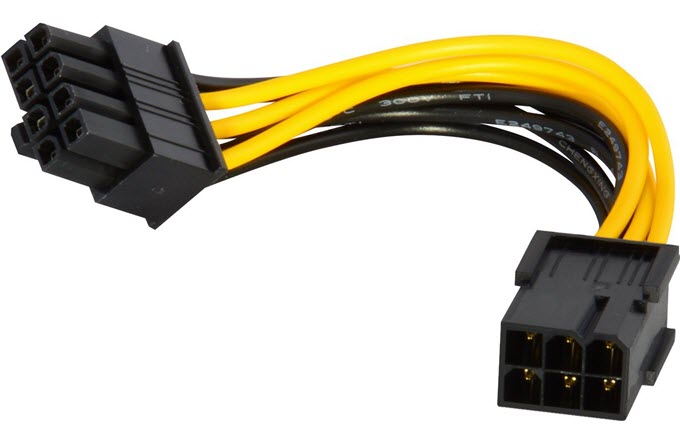

If your GPU requires an 8-pin input but you only have a 6-pin cable available, this adapter can work. However, be careful: a 6-pin cable is rated for 75W, while the 8-pin device expects 150W. Only use this if you are sure your PSU’s 6-pin cable is high quality and the rail can handle the extra load.
4. SATA to 6-Pin/8-Pin PCI-E Adapters (Use Caution!)


⚠️ Safety Warning
Molex connectors are generally safer than SATA connectors for high-power GPUs. SATA connectors are rated for lower continuous current than Molex or PCIe pins. Using a SATA-to-8-pin adapter can lead to melted wires or fire hazards if the GPU draws significant power. Use these only as a last resort for lower-power cards.
Power Consumption Chart
The table below summarizes the maximum power a graphics card can draw based on its connector configuration.
| PCI Express x16 | 6-Pin Connector | 8-Pin Connector | Total Max Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| 75W | – | – | 75W |
| 75W | 1 x 75W | – | 150W |
| 75W | – | 1 x 150W | 225W |
| 75W | 2 x 75W | – | 225W |
| 75W | 1 x 75W | 1 x 150W | 300W |
| 75W | – | 2 x 150W | 375W |
If you have any queries or doubts regarding graphics cards or their power consumption then feel free to ask me by leaving a comment below.
You can also check the following for best graphics cards for your new build.

A passionate tech enthusiast with a deep focus on PC hardware, gaming rigs, and performance tuning, Bertine Gaynor has spent years exploring the latest innovations in processors, GPUs, and custom builds. On DigitalUpbeat.com, he shares hands-on reviews, performance breakdowns, and expert insights to help readers make smart hardware choices. When not testing components, he’s often optimizing setups for peak efficiency or diving into the latest tech trends shaping the future of computing.


